In our quest for optimal health and wellness, one nutrient stands out as the cornerstone of our dietary needs: protein. Whether you’re an athlete looking to build muscle, someone aiming to lose weight, or just trying to find a balanced diet, this blog is essential to understanding the importance of protein importance under why protein is important for our body, protein sources, and how it is made you can incorporate more into your daily diet learning in detail.
What is a protein?

Protein is one of the three macronutrients along with carbohydrates and fats. It is made up of amino acids, which are life-binding compounds. There are 20 amino acids, nine of which are considered essential because our bodies cannot make them. This means we need to get them from our diet. Proteins play a variety of roles in the body, from repairing tissues to producing enzymes and hormones.
Role of proteins in the body:
Muscle growth and repair:

One of the best known functions of proteins is their role in muscle formation and repair. When we engage in physical activity, especially strength training, we create small tears in our muscle fibers. Protein helps repair these tears, promoting muscle growth and strength.
Weight Management:

Protein can be a powerful ally in weight management. Protein-rich foods are more filling, and can help reduce overall caloric intake. In addition, the heat of protein—the energy needed to digest and process protein—is greater than that of carbohydrates and fats, which means more calories are burned when processing protein-rich foods
Supports immune system function:

Proteins are used to make antibodies that help fight infections and diseases. Adequate protein intake is essential to maintain a strong immune system, and improve your immune system.
Production:
Many cells in the body produce proteins such as insulin that regulate blood sugar levels. Adequate protein intake is essential for the production of these hormones, which helps the body maintain various functions.
Healthy skin, hair and nails:

Proteins like collagen and keratin are important for healthy skin, hair and nails. A protein-poor diet can lead to brittle nails, hair loss and dull skin.
Protein sources:
Protein can be obtained from a variety of food sources, which can be classified as proteins of animal and plant origin.
Animal-derived proteins Meat: Beef, chicken, pork and lamb are good sources of protein. Thinner cuts are ideal for those who want to control fat intake.

Fish and Seafood: Fish like salmon, tuna and trout are not only rich in protein but also packed with omega-3 fatty acids that have many health benefits
Dairy products: Milk, yogurt and cheese are great sources of protein and calcium. Greek yogurt, in particular, contains more protein compared to regular yogurt.
Eggs: Eggs are a healthy source of nutrients, and provide a complete source of protein. It also contains nine essential amino acids, making it an ideal addition to any diet.
Proteins of plant origin:
Legumes: Potatoes, legumes and chickpeas are wonderful sources of plant-based protein. It is also high in fiber, which aids in digestion and digestion.
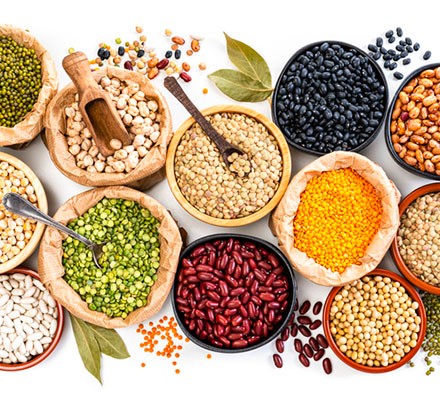

Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds and flaxseeds provide a decent amount of protein along with healthy fats. Easily added to smoothies, salads, or as a snack.
Whole grains: Quinoa, brown rice and oats are high in protein and provide essential nutrients and fiber.
Soy products: Tofu, tempeh and edamame are good sources of protein for those who follow a vegetarian diet.
How much protein do you need?
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for protein varies based on age, sex, and level of physical activity. The RDA for an average adult is about 0.8 grams of protein per pound of body weight. However, athletes or those involved in vigorous exercise may require more, typically 1.2 to 2.0 grams per kilogram of body weight.
Tips to increase protein intake:

Include Protein in Every Meal: Make a conscious effort to include a source of protein with every meal. Whether it’s eggs for breakfast, chicken for lunch, or beans for dinner, protein supplements can help meet your daily needs.
Smart snacks: Opt for protein-packed snacks like Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, or a handful of fruit instead of chips or candy.
Choose whole foods: Focus on whole foods that are highly processed and rich in nutrients. Foods like quinoa, legumes and lean meats provide not only protein but also other essential nutrients.
Use a protein supplement: If you struggle to meet your protein needs through food alone, consider a protein powder or bar. These can be relevant, especially for post-exercise recovery.
Conclusion:
Protein is an essential nutrient that plays many roles in maintaining our health and wellbeing. Whether you’re aiming to build muscle, lose weight, or just live a healthy lifestyle, making sure you eat the right amount of protein is important. By incorporating proteins into your diet and being mindful of your protein intake, you can unlock the many benefits of this powerful nutrient. So, embrace the power of protein, and watch your health improve!

