
Introduction
Addiction is a pervasive issue that affects individuals across the globe, irrespective of age, gender, or background. Defined as the compulsive engagement in a behavior or use of a substance despite negative consequences, addiction can encompass a wide range of habits, from substance abuse to behavioral addictions like gambling and technology dependence. In modern society, the prevalence of addiction has reached alarming levels, impacting not only the individuals directly involved but also their families and communities. Breaking these destructive habits is of paramount importance, as it paves the way for a healthier, more fulfilling life. This article delves into effective strategies for overcoming addictions and building a new path toward positive change.
Understanding Addiction: The Science Behind It
How addiction affects the brain

At the heart of addiction lies a complex interplay of neurological processes. The brain’s reward system, driven by the neurotransmitter dopamine, reinforces pleasurable behaviors and creates a cycle that becomes difficult to break. Understanding the way addictive substances and behaviors hijack this system is essential to devising effective strategies for combating addiction.
The dopamine reward system
Dopamine, often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, plays a central role in addiction. Continuous engagement in addictive activities floods the brain with dopamine, creating an intense craving for the behavior. Over time, this leads to tolerance, requiring more of the substance or behavior to achieve the same pleasurable effects.
The role of genetics and environment in addiction
Genetic predisposition and environmental factors both contribute to an individual’s susceptibility to addiction. Certain genetic traits can increase the likelihood of developing addictive behaviors, while factors like early exposure, trauma, and social environment also play a significant role in shaping addictive tendencies.
The different types of addiction

Addiction isn’t limited to substances like drugs or alcohol; it extends to behaviors as well. From gambling to overeating, shopping to excessive screen time, behavioral addictions share similar underlying mechanisms with substance-based ones. Recognizing these various forms of addiction is crucial for effective intervention.
Recognizing and Acknowledging Bad Habits/Addictions
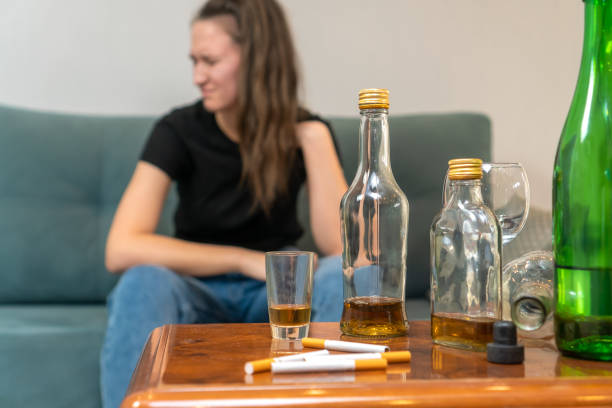

Identifying the signs of addiction

Recognizing addiction requires a keen awareness of the signs. These may include loss of control over the behavior, neglect of responsibilities, withdrawal symptoms, and strained relationships. Acknowledging these signs in oneself or others is the first step toward change.
Self-reflection and self-awareness

Gaining insight into the reasons behind addictive behaviors demands self-reflection. Exploring underlying emotions, triggers, and patterns helps individuals understand the root causes of their habits, enabling them to tackle the problem at its source.
Understanding the consequences of bad habits

Confronting the harsh realities of addiction is necessary to fuel motivation for change. Examining the negative impact of addiction on physical health, mental well-being, relationships, and overall quality of life serves as a powerful catalyst for transformation.
Overcoming denial and accepting the need for change

Denial often acts as a barrier to recovery. Acknowledging the existence and severity of the addiction requires courage and honesty. Acceptance paves the way for seeking help and embracing change.
Building Motivation and Commitment

Finding your “why”
Motivation is the driving force behind change. Identifying deeply personal reasons for breaking free from addiction strengthens commitment and resilience. Whether it’s rebuilding relationships, pursuing passions, or regaining self-worth, finding a compelling “why” fuels the journey.
Setting SMART goals

Clear goals are essential to track progress and stay on course. SMART goals are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. They provide a roadmap for change, ensuring each step is purposeful and manageable.
Visualizing your successful journey

Visualization harnesses the power of the mind to manifest change. Envisioning a life free from addiction enhances motivation and creates a positive outlook, helping individuals stay focused on the destination.
Cultivating a support system

Embarking on the journey alone can be daunting. A strong support system of friends, family, or support groups provides encouragement, accountability, and a safe space to share struggles and successes.
Seeking Professional Help: Therapy and Counseling
Different types of therapy

Therapy forms a cornerstone of addiction recovery. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps reshape thought patterns and behaviors, while Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) focuses on emotional regulation. Exploring the options and finding a suitable approach is key.
Benefits of therapy in overcoming addiction

Therapy equips individuals with coping mechanisms, stress management tools, and strategies to navigate triggers. It addresses underlying psychological factors that contribute to addiction, fostering lasting change.
Finding a suitable therapist/counselor

The therapeutic relationship is crucial. Finding a therapist who understands addiction, connects with the individual, and creates a judgment-free environment is pivotal to successful recovery.
Group therapy and support groups

Group settings offer a sense of belonging and shared experience. Engaging with peers facing similar challenges provides validation, empathy, and an avenue for learning from others’ strategies.
Developing Healthy Coping Mechanisms

Identifying triggers and high-risk situations
Recognizing situations, emotions, and environments that trigger addictive behaviors is vital. Armed with this awareness, individuals can proactively develop strategies to manage and navigate these triggers.
Alternative activities and hobbies
Replacing addictive behaviors with constructive alternatives is effective in breaking the cycle. Engaging in hobbies, sports, or creative pursuits not only distracts from cravings but also nurtures personal growth.
Stress management techniques
Stress often drives addictive behaviors. Learning stress management techniques such as meditation, exercise, deep breathing, and mindfulness empowers individuals to address stressors in healthier ways.
Building and maintaining healthy relationships
Healthy relationships provide essential support. Rebuilding trust, communication, and connection with loved ones fosters a strong support network and reduces feelings of isolation.
Making Lifestyle Changes

Developing a structured routine
Structure brings stability to recovery. Establishing a daily routine minimizes idle time, which can lead to relapse, and provides a sense of purpose and accomplishment.
Practicing self-care and self-compassion
Self-care is paramount. Nurturing physical, emotional, and mental well-being through proper sleep, nutrition, and self-compassion strengthens resilience and self-worth.
Incorporating exercise and physical activity
Exercise releases endorphins, promoting feelings of happiness and reducing cravings. Regular physical activity is linked to improved mood, reduced stress, and enhanced self-esteem.
Healthy eating habits and nutrition
Nutrition plays a role in mental health. Adopting a balanced diet rich in nutrients supports brain function and emotional stability, aiding in the recovery process.
Adopting Cognitive and Behavioral Strategies
Challenging and changing negative thoughts
Negative thought patterns perpetuate addiction. Learning to challenge and reframe these thoughts empowers individuals to develop healthier perspectives and coping mechanisms.
Developing positive affirmations
Positive affirmations enhance self-belief. Replacing self-destructive self-talk with empowering affirmations cultivates a sense of agency and fosters a positive self-image.
The power of self-talk and self-belief
Self-talk shapes behavior. Cultivating a habit of positive self-talk enhances self-esteem, reduces self-criticism, and bolsters the belief in one’s capacity for change.
Behavioral techniques
Replacing addictive behaviors with healthier habits is effective. Implementing reward systems for reaching milestones and substituting destructive habits with constructive ones reinforces positive change.
Dealing with Relapse and Setbacks

Understanding the
nature of addiction relapse
Relapse is a common part of the recovery journey. Understanding that it’s not a sign of failure but a setback helps individuals approach it with compassion and learn from it.
Coping with setbacks and learning from them
Setbacks offer valuable insights. Analyzing triggers, emotions, and circumstances leading to relapse helps individuals develop strategies to prevent recurrence.
Implementing strategies to prevent future relapses
Learning from relapses, individuals can refine their coping mechanisms and develop an action plan to navigate future challenges effectively.
Seeking support and professional help during challenging times
During difficult periods, reaching out for help is vital. Whether from a therapist, support group, or loved ones, seeking assistance reinforces resilience and prevents isolation.
Conclusion
Breaking bad habits and overcoming addiction is a journey that demands patience, perseverance, and dedication. Armed with a deeper understanding of addiction’s mechanisms and a comprehensive toolkit of strategies, individuals can embark on a transformative path toward lasting change. It’s crucial to remember that setbacks are not roadblocks but opportunities for growth. By embracing the strategies outlined in this article, individuals can rewrite their narratives, build healthier lives, and experience the freedom that comes from breaking the chains of addiction. The road may be challenging, but with unwavering persistence, self-compassion, and the support of others, the destination of a fulfilling, addiction-free life is within reach.
