Maintaining a vibrant metabolic rate is central to the pursuit of optimal health. Metabolism, the process by which your body converts what you eat and drink into energy, plays an important role in weight management, maintaining energy levels, and overall well-being If you have figured out how to fuel your body once the variable has become slightly larger, you are not alone. More and more people are looking for effective ways to boost their metabolism and, by extension, their health and vitality. In this blog, we’ll explore the most effective metabolic boosters that are backed by science and ready to boost your energy levels yet again.
Understanding cellular metabolism:
Before we get into boosters, let’s clearly define what metabolism is. Many factors affect your metabolism, including age, gender, muscle weight and activity level. Basically, a better metabolism means your body burns more calories, which can help with weight management and energy levels.
1. High intensity interval training (HIIT)

When it comes to metabolic worster, exercise is one of the cornerstones. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) stands out as a particularly powerful way to increase your metabolism. HIIT consists of short bursts of intense exercise followed by periods of rest or low-intensity exercise. This type of exercise not only burns more calories during the workout, it also burns increased calories post-workout—a process known as oxygen consumption excessive activity after exercise (EPOC).
Studies have shown that HIIT can raise your metabolic rate for hours after your workout. This means that your body is burning more calories even when you are resting. When incorporated into a weekly routine, HIIT can provide significant improvements in both aerobic and anaerobic fitness, making it a powerful tool for increasing metabolism.
2. Green tea
Green tea has long been lauded for its health benefits, with one notable benefit being its metabolic effects. Green tea contains catechins, especially epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which have been shown to increase lipid metabolism and accelerate metabolism.
Research shows that drinking green tea can slightly increase calorie burn. The combination of caffeine and catechins is thought to be responsible for this effect. In addition, green tea is rich in antioxidants, which can benefit overall health and well-being. Consider drinking a cup of green tea in the morning or as an afternoon pick me up to improve your metabolism.
3. Protein rich foods
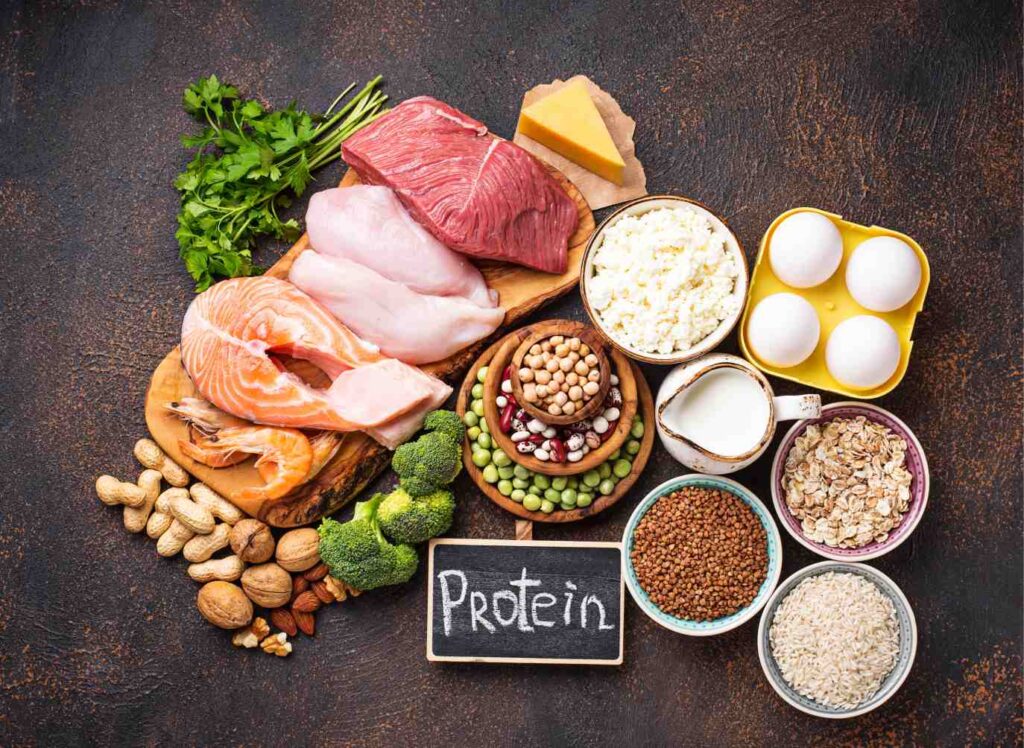

The heat gain of food (TEF) refers to the energy required to synthesize, absorb, and process nutrients from food. Compared to fats and carbohydrates, protein has a higher TEF, which means your body burns more calories when digesting protein-rich foods. So, adding protein to your diet can help boost your metabolism.
Some good sources of protein include lean meats, eggs, dairy, nuts and berries. The supplementation of these foods can help preserve muscles that are essential for proper metabolism. Because muscle tissue burns more calories at rest compared to adipose tissue, increased muscle mass may contribute to increased resting metabolism.
4. Spicy foods: What Helps the Digestive System
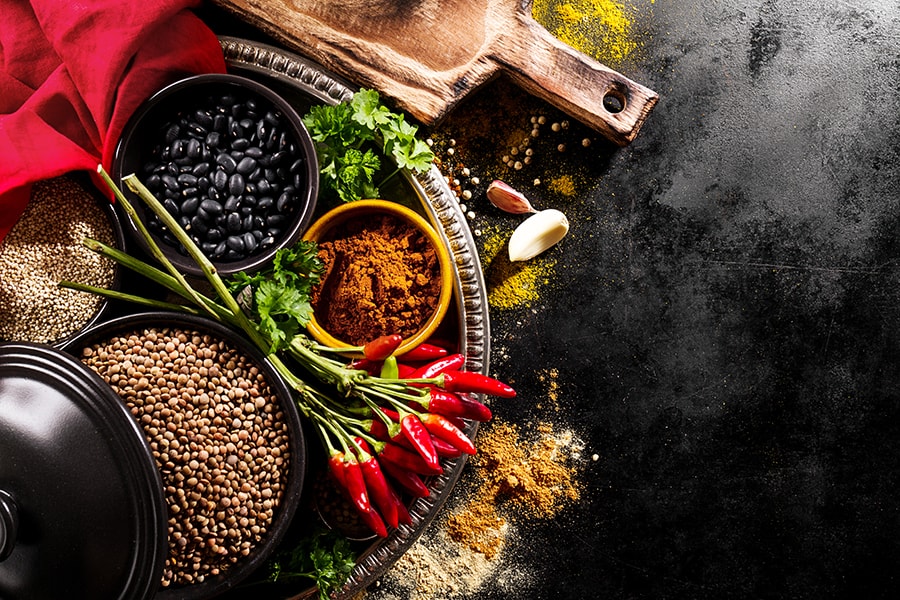

If you get some heat in your diet, you’ll be happy to know that spicy foods can temporarily boost your metabolism. Capsaicin, the inflammatory compound in spinach, has been shown to increase metabolism and increase fat oxidation.
Studies have shown that eating spicy foods can cause a temporary increase in metabolism. While the effect may be small, adding spicy ingredients can provide a delicious way to boost your metabolism. Just focus on your endurance and overall health, especially if you have stomach issues.
5. Adequate Hydration

Hydration is often overlooked when it comes to metabolism, but proper hydration is essential to maintaining a healthy metabolism. The lack of water can slow down your metabolism, making it harder for your body to burn calories efficiently.
Drinking cold water can provide additional benefits; Your body expends energy to heat water for body heat, increasing calorie burn slightly. Make it a point to drink plenty of water throughout the day, and consider starting your morning with a glass of water to kick-start your metabolism.
6. Adequate Sleep

Sleep is an important metabolic factor that is often taken for granted. Poor sleep can disrupt hormone levels, including those that regulate hunger and metabolism. Lack of sleep can increase your appetite and your cravings for high-calorie foods, which can negatively affect your metabolism. Making sure you get enough quality sleep is important for a healthy metabolism. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night, and establish a consistent sleep schedule that supports your body’s natural muscle tone. Creating a comfortable environment and good sleep hygiene practices can make your sleep better again.
7. Caffeine: A metabolic stimulator

Caffeine is a well-known stimulant that can temporarily increase metabolism. Caffeine, found in coffee, tea and energy drinks, increases your heart rate and stimulates the central nervous system, temporarily increasing metabolism
Studies show that caffeine can increase caloric expenditure and fat oxidation, making it a useful metabolic boosting tool. However, moderation is key, as caffeine overdose can have side effects such as anxiety, restlessness and insomnia.
8. Intermittent fasting

Intermittent fasting (IF) is a pattern of alternating periods of eating and fasting. Although the primary goal of IF is usually weight management, it can also affect metabolism. When you are fasting, your body turns to burning fat for energy, which can help boost your metabolism
Research on intermittent fasting suggests that it can improve metabolic markers such as insulin sensitivity and fat oxidation. When considering IF, it’s important to choose a fasting program that suits your lifestyle and to consult with a health care provider if you have any underlying health conditions.
Conclusion
You don’t need drastic changes or extremes to boost your metabolism. By incorporating these science-backed strategies into your routine—from exercise to dietary changes to lifestyle changes—you can raise your metabolism and get energy flowing high and improved health. Remember that consistency is key, and combining several of these methods will give you the best results. Embrace these metabolites and get ready to regain your strength and vitality!
FAQS
1. How long does it take to see metabolic results?
Answer: The time it takes to see results from metabolic boosters can vary depending on a lot of factors, including the specific regimen, your overall health, how compatible you are with the regimen for example , incorporating high-intensity interval training (HIIT) into your routine and noticing metabolic changes over a few weeks can indicate improvement, while changes from dietary changes, such as protein increasing or drinking green tea may take a little longer to manifest It is important to take metabolic strategies as part of long-term lifestyle changes rather than expectations for immediate results. Continued long-term efforts will yield the most important benefits.
2. Are there any risks associated with the use of hormones?
Answer: While most metabolic procedures are generally safe when used appropriately, there are some risks to be aware of. For example, excessive consumption of caffeine can lead to problems such as anxiety, insomnia and heart palpitations. Similarly, excessively intense exercise without adequate rest and recovery can increase the risk of injury or burns. It’s important to use these techniques sparingly and listen to your body. If you have any health conditions or concerns, consult with a health care provider before making drastic changes to your diet or exercise routine.

